| Lesson 2 | Hierarchical and relational databases |
| Objective | Describe the characteristics of hierarchical and relational databases. |
Hierarchical and Relational Databases
It is essential to provide students with a clear, high-level overview of different database models.
Two fundamental types are hierarchical databases and relational databases, each with distinct characteristics and use cases.
- Hierarchical Databases:
- Structure: Hierarchical databases organize data in a tree-like structure, akin to a family tree. Each record, or 'node', has a single parent, except for the root node at the top of the hierarchy. This structure creates a parent-child relationship among data items.
- Data Model: The model is straightforward and intuitive, representing one-to-many relationships. It is suitable for representing information with a hierarchical relationship, such as organizational structures or file systems.
- Access and Navigation: Data access in a hierarchical database is top-down, starting from the root node and moving down the hierarchy. This model supports efficient data retrieval when the path is well-defined.
- Data Integrity: Since the hierarchical structure is rigid, it inherently maintains data integrity. Each child node has precisely one parent, which helps in preserving the consistency of data.
- Limitations: The hierarchical database model is less flexible in handling many-to-many relationships and can lead to data redundancy. Moreover, it is not as adaptable to changes in the data structure as other models.
- Relational Databases:
- Structure: Relational databases store data in tables (or relations), where each table consists of rows (records) and columns (attributes). This structure provides a more flexible and normalized approach to data management.
- Data Model: The relational model is based on the concept of set theory and supports a wide range of data types. It excels in handling both one-to-many and many-to-many relationships.
- Access and Manipulation: Data in relational databases is accessed and manipulated using Structured Query Language (SQL). SQL provides a powerful and versatile way to query, update, insert, and delete data across multiple tables.
- Data Integrity and Normalization: Relational databases allow for data normalization, a process of structuring data to reduce redundancy and improve integrity. They also support constraints, like primary keys and foreign keys, to maintain data accuracy and consistency.
- Flexibility and Scalability: These databases are highly flexible and scalable. They can efficiently handle large amounts of data and complex queries, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Hierarchical databases
Hierarchical databases are based on "parent/child" (or top-down) relationships among data elements.
The logic in this arrangement is that a child may have only one "parent," but a "parent" may have more than one "child." Hierarchical databases are rigid, which makes them easy to maintain but difficult to query.
Hierarchical databases have been used for core business applications such as payroll, accounts receivable, and accounts payable. The figure below shows how a simple order placed on a web site has to work its way down a hierarchical structure.
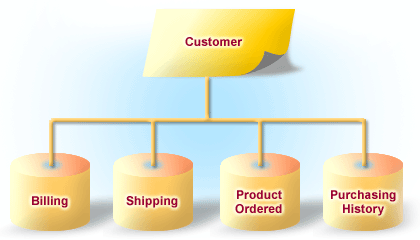
IBM's IMS (Information Management System) is one example of a proprietary hierarchical database software package.
Relational databases
Relational databases are based on the metaphor of a basic table with rows and columns. Data elements stored in these "tables" share a relationship defined by a common element, called a key. For example, the same product number (key) may be used by programs that process and ship orders, track inventory, update pricing, and so on.
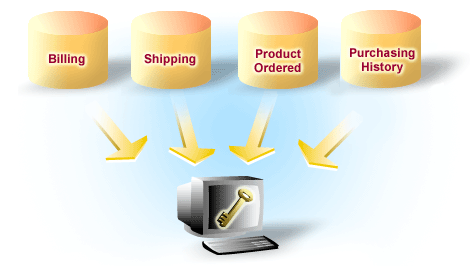
The figure below illustrates how a product number (the key) entered by a customer on a Web site accesses many data sources simultaneously.
Relational database: Database based on the metaphor of a basic table with rows and columns. Data elements stored in these "tables" share a relationship defined by a common element called a key.
The figure below illustrates how a product number (the key) entered by a customer on a Web site accesses many data sources simultaneously.
Relational database: Database based on the metaphor of a basic table with rows and columns. Data elements stored in these "tables" share a relationship defined by a common element called a key.
Examples of relational database products include:
- IBM DB2
- Informix SQL
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Oracle
Database Characteristics
Click the link below to increase your understanding of the differences between hierarchical[1] and relational databases.
Database Characteristics
Database Characteristics
[1]Hierarchical database: Database based on top-down relationships among data elements. Hierarchical databases are used for core business applications such as payroll and accounts receivable.