Lesson 14
Elements which influence E-Business Architectural Drivers
| Element | Influence on Architectural Drivers |
|---|---|
| Consumerism | Technology shifts (e.g., mobile, AI, IoT) empower consumers with more choice, convenience, and control. Architecture must prioritize user-centric designs, scalable personalization, real-time access, and omnichannel support. |
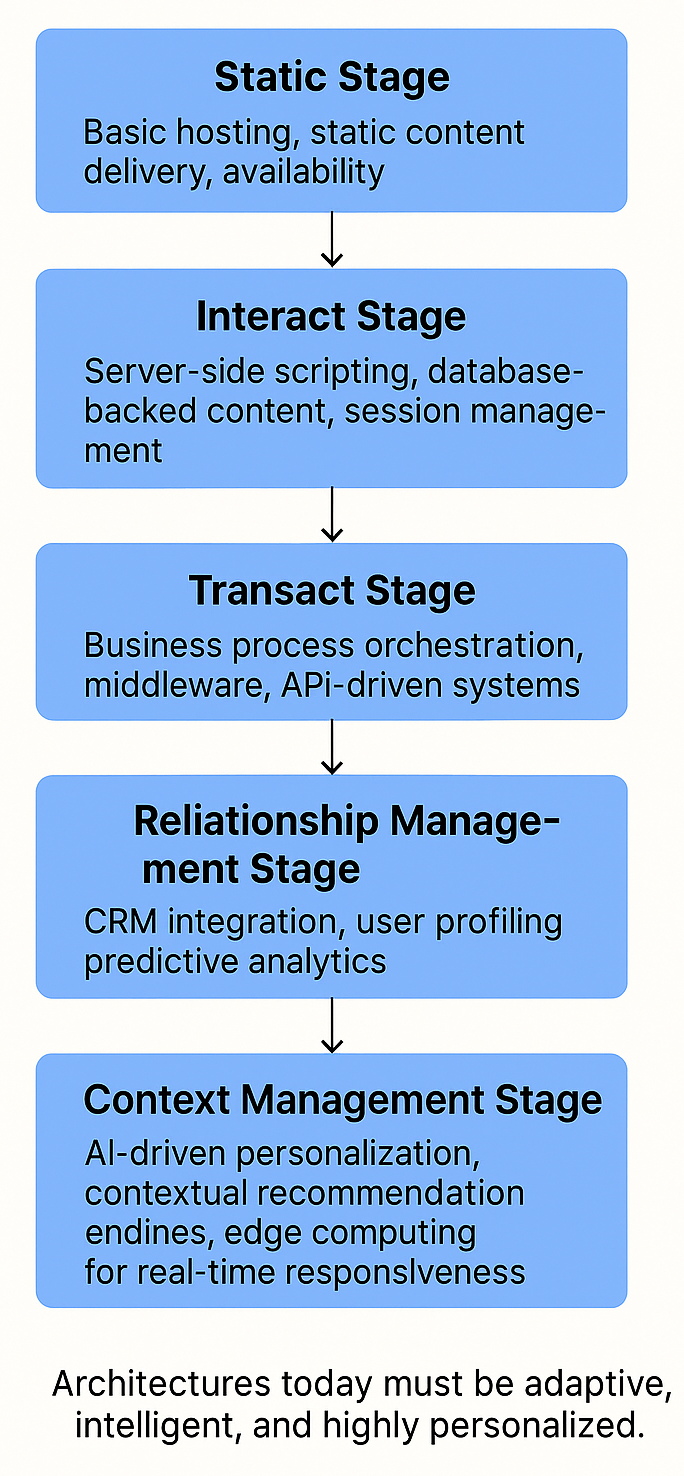
| Historical Market Flow | E-business architecture must evolve based on lessons learned from the stages below. Architectures move from basic static websites to highly dynamic, contextual platforms with AI-driven personalization. |
| Static Stage (early web) | Simple, static websites. Architectural drivers focused on basic hosting, static content delivery, availability. Minimal concern for interactivity or dynamic content. |
| Interact Stage | Need for two-way communication (e.g., forms, email inquiries). Architecture had to support basic server-side scripting and database-backed content. Begin shaping session management and early personalization. |
| Transact Stage | E-commerce starts: secure transactions, shopping carts, authentication. Architectural drivers shift to security, reliability, payment integration, and scalability for spikes (sales, promotions). |
| Enact Stage | Complex workflows (e.g., B2B ordering, supply chain integration). Architecture expands to include business process orchestration, middleware, service buses, and API-driven systems. |
| Relationship Management Stage | Focus on customer loyalty and personalization. Drivers now include CRM integration, user profiling, predictive analytics, and marketing automation systems. |
| Context Management Stage | Delivering the right content, at the right time, in the right context. Drivers evolve towards AI/ML, contextual recommendation engines, dynamic personalization, and edge computing for responsiveness. |
| Competitive Landscape | Fierce competition forces architectures to prioritize agility, rapid innovation, continuous deployment, resilience, and platform-based ecosystems (e.g., marketplaces, app stores, plug-and-play services). |
Summary of Evolution
-
Early static architectures → focused mainly on content delivery.
- Interact and Transact stages → introduced transaction security, session management, and scalable databases.
- Enact and Relationship Management → demanded integration across systems, orchestration, and customer intelligence.
- Context Management → today's challenge: hyper-personalization, real-time AI processing, multi-cloud, and edge architectures.
- Competitive pressure accelerates the shift toward resilient, adaptive, and service-based architectures (microservices, serverless, containerization).
Market research for on-line shopping carts indicates that users are loading their carts, but are not completing their transactions.
Define the meaning for each of the following consumer expectations.
In short: Modern consumers expect fast, high-quality, customized, proactive, and competitively priced experiences, and if they sense friction (slow checkout, unclear pricing, no personalization), they will abandon their carts.
- Instant gratification
- Global best price
- Global best quality
- Personal customization
- Pre-emptive service Global best price
| Label | Expectation |
|---|---|
| A. Instant gratification | Consumers expect immediate results or delivery. In the context of online shopping, this means fast page loads, instant checkout, rapid order confirmation, and, ideally, same-day or next-day shipping. |
| B. Global best quality | Consumers expect the highest available product quality, not just locally but compared globally. They want assurances that the item they’re purchasing is among the best products offered anywhere in the world. |
| C. Personal customization | Consumers want tailored experiences and products. This can include personalized recommendations, the ability to customize products (e.g., colors, features), or dynamic interfaces that adapt to their shopping habits. |
| D. Pre-emptive service | Businesses are expected to anticipate customer needs before they arise. This means proactive customer support (e.g., live chat offers help before the user asks), predictive shipping estimates, or early alerts for discounts, upgrades, or issues. |
| E. Global best price | Consumers expect that they are getting the lowest possible price available internationally. They often compare prices across regions and expect transparent, competitive pricing without hidden fees. |
In short: Modern consumers expect fast, high-quality, customized, proactive, and competitively priced experiences, and if they sense friction (slow checkout, unclear pricing, no personalization), they will abandon their carts.
This module covered the drivers that guide an engagement and e-Business.
In the next module we will explore how companies are using the Internet and its technologies to deliver e-Business.
To verify your understanding of concepts covered in this module, we recommend that you take the end of module self-check quiz.
Not only will this help verify your own understanding, but it will provide you with valuable practice prior to taking the end of course test.
Consumer Expectation - Quiz
To verify your understanding of concepts covered in this module, we recommend that you take the end of module self-check quiz.
Not only will this help verify your own understanding, but it will provide you with valuable practice prior to taking the end of course test.
Consumer Expectation - Quiz