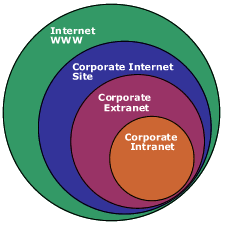
The rise of intranets and extranets has fundamentally reshaped the contours of e-business, driving operational efficiency, enhancing collaboration, and fostering robust business relationships. The integration of these networks with cutting-edge internet technologies underpins the seamless exchange of information, seamless communication, and streamlined business processes, fortifying the e-business ecosystem.
The Intranet: Bolstering Internal Communication and Collaboration
Definition and Purpose Intranets, private networks confined within an organization, serve as central hubs for internal communication, information dissemination, and collaborative endeavors.Impact on E-Business
- Enhanced Communication: Intranets facilitate seamless internal communication, ensuring that employees are well-informed and aligned with organizational objectives.
- Collaborative Workspace: They provide platforms for collaborative work, allowing teams to coordinate effectively, share information, and manage projects, amplifying operational efficiency.
- Knowledge Management: Intranets support comprehensive knowledge management, ensuring that critical information and resources are readily accessible to employees, fostering informed decision-making.
- Administrative Efficiency: Automated administrative processes on intranets free up valuable resources and time, contributing to enhanced productivity and operational efficacy.
The Extranet: Strengthening External Business Relationships
Definition and Purpose Extranets extend the intranet beyond the organizational boundaries, offering selective access to external stakeholders such as suppliers, partners, and customers.Impact on E-Business
- Enhanced Supply Chain Management: Extranets optimize supply chain management by providing vendors and suppliers real-time access to pertinent information, ensuring timely and efficient supply chain operations.
- Strengthened Business Partnerships: They fortify business relationships by offering a centralized platform for communication, collaboration, and information exchange with partners and affiliates.
- Customer Engagement and Support: Extranets enhance customer engagement and support by providing customers access to tailored resources, information, and services.
- Secure Information Sharing: They enable secure and controlled sharing of sensitive information with external stakeholders, bolstering trust and collaboration.
Integration with Internet Technologies
Scalability and Accessibility
The confluence of intranets and extranets with internet technologies ensures scalability and accessibility. Cloud integration allows organizations to expand their networks seamlessly, providing global accessibility and ensuring uninterrupted operations.Enhanced Security
Incorporating advanced internet security protocols safeguards intranets and extranets against unauthorized access and cyber threats, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of business information.
Integration with E-Business Systems
The seamless integration of intranets and extranets with various e-business systems and platforms, such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, streamlines business operations and enhances organizational efficiency.
In essence, intranets and extranets occupy a critical role in shaping the e-business landscape. Their seamless integration with advanced internet technologies amplifies their impact, driving operational efficiency, fostering collaboration, and strengthening internal and external business relationships. In the digital age, the strategic deployment of intranets and extranets is paramount for e-businesses aspiring to thrive in a competitive and interconnected global marketplace.