| Lesson 3 | Selecting an eBusiness model for B2B |
| Objective | Identify the various B2B models available |
Selecting e-business Model for B2B
Establishing an e-business model helps the enterprise identify its purpose. Because it helps to identify how a business connects the activities in its value chain more cheaply or more adeptly than its competitors, it in some ways determines how efficiently the business invents or reinvents itself. An e-business model may vary in complexity, from the simplest forms that involve a business selling goods and services directly to customers, to the more complex forms that involve facilitators and brokers.
- B2B Models differentiate themselves on Three Levels
B2B models aim at 1) low-entry cost, 2) functionality, and 3) more comprehensive automation of business cycle, and differentiate themselves on three levels.- Business process: for example, supply chain management, distribution channel management and procurement
A business process is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks that produce a specific service or product (serve a particular goal) for a particular customer or customers. It can often be visualized with a flowchart as a sequence of activities with interleaving decision points or with a Process Matrix as a sequence of activities with relevance rules based on data in the process. - Method: for example, EDI, Web-EDI, Internet. (EDI) Electronic data interchange is an electronic communication system that provides standards for exchanging data by means of any electronic means. By adhering to the same standard, two different companies in two different countries can electronically exchange documents (such as purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices). EDI has existed for more than 30 years and there are many EDI standards, some of which address the needs of specific industries or regions.
It also refers specifically to a family of standards. - Type: for example, software, implementation services and ongoing services
- Business process: for example, supply chain management, distribution channel management and procurement
Merits and Limitations of B2B ecommerce
Merits of B2B E-commerce:
Limitations of B2B E-commerce:
In conclusion, while B2B e-commerce offers numerous advantages such as efficiency, cost reduction, and expanded market reach, it also comes with challenges like complex integration, security concerns, and the need for a robust technological infrastructure. Businesses must carefully weigh these factors when considering their e-commerce strategies.
- Expanded Market Access: B2B e-commerce potentially widens the market reach of businesses. By leveraging digital platforms, companies can access global markets more easily than through traditional channels.
- Efficiency in Operations: It automates and streamlines business processes, leading to increased efficiency. This efficiency can be seen in order processing, customer service, and supply chain management.
- Cost Reduction: There's a significant reduction in costs associated with marketing, customer service, and inventory management. The digital nature of e-commerce minimizes the need for physical stores and reduces paper-based processes.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: E-commerce platforms can provide valuable data analytics. This data helps in understanding market trends, customer preferences, and buying patterns, aiding in more informed decision-making.
- Personalization and Customer Relationship Management: B2B e-commerce platforms allow for customized experiences for business clients, which can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Limitations of B2B E-commerce:
- Complex Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating e-commerce platforms with existing business systems and processes can be complex and costly, especially for businesses with legacy systems.
- Security Concerns: There are significant security concerns, including data breaches and cyber-attacks. Maintaining high levels of security to protect sensitive business information is crucial but challenging.
- Limited Human Interaction: The lack of personal interaction can be a downside in B2B relationships where trust and long-term partnerships are vital. This limitation can affect negotiation processes and relationship building.
- Dependency on Technology: There's a heavy reliance on the technological infrastructure. Any downtime or technical issues can disrupt business operations and lead to losses.
- Market Saturation and Competition: The ease of entering e-commerce has led to saturated markets in some sectors. This saturation increases competition and can pressure profit margins.
In conclusion, while B2B e-commerce offers numerous advantages such as efficiency, cost reduction, and expanded market reach, it also comes with challenges like complex integration, security concerns, and the need for a robust technological infrastructure. Businesses must carefully weigh these factors when considering their e-commerce strategies.
- It pays to be Adaptable: Although the concept of business models is not new, e-business has in many ways rewritten the rules and introduced new and exciting possibilities. The same motto applies to B2B e-business models: it pays to be adaptable. With hybrids and new ideas emerging continually, it is impossible to discuss or define every possible option. We will first look at the primary B2B model, then at the more common specialized versions.
- The primary B2B Model: Within the primary B2B model, there are many model variations that the architect must address. We will discuss some of the more common ones. e-business B2B models are interfaces between businesses. The models applied to B2B e-business are often similar to those used in B2C e-business, and some may apply to both. Examples include the Brokerage and Advertising models, which we will address in later lessons. Let us now look at specialized B2B models.
- Specialized B2B models are required when a business is an intermediary or hub[1].
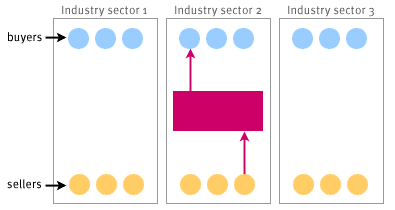
Hubs link businesses and provide benefit by aggregating buyers and/or sellers. B2B hubs can focus either vertically or horizontally, as shown in the following image. Horizontal hubs are also known as functional hubs.
Vertical Horizontal B2B Hubs
Vertical Horizontal B2B Hubs
You may view a printable version of the B2B hubs table by clicking the icon to the left.
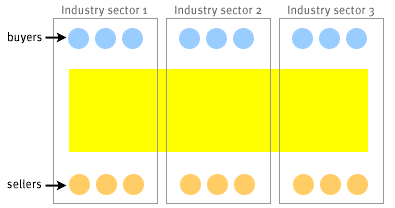
As you can see, there are marked differences between horizontal and vertical hubs. The SlideShow below describes examples of each.
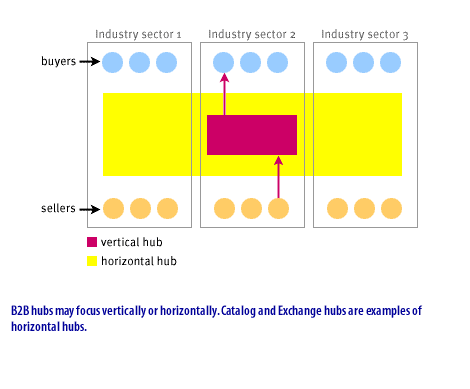
- B2B hubs may focus vertically or horizontally. Catalog and exchange hubs are examples of horizontal hubs.
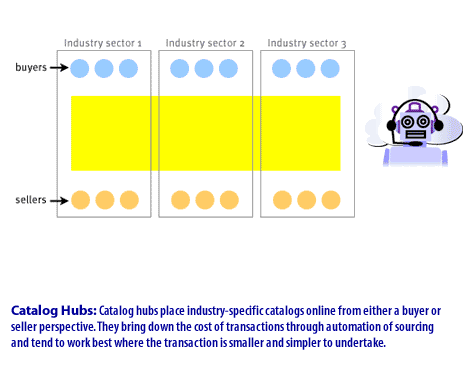
- Catalog Hubs place industry-specific catalogs online from either a buyer or seller perspective.
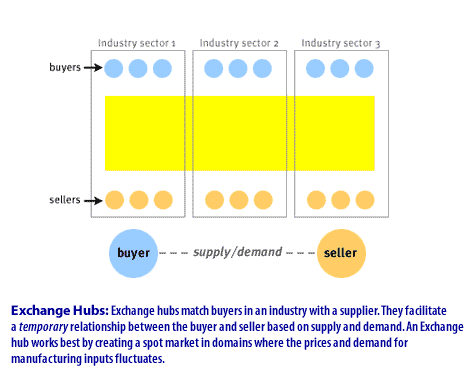
- Exchange hubs match buyers in an industry with a supplier.
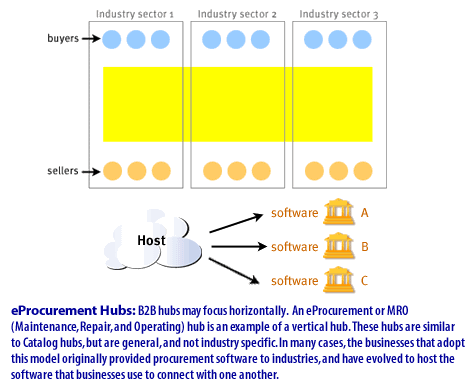
- b2b hubs may focus horizontally. An e-procurement hub or MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Operating) hub is an example of a vertical hub.
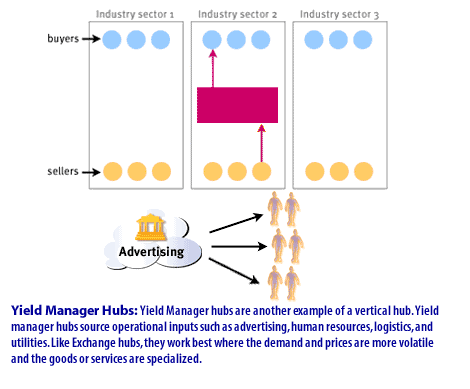
- Yield Manager Hubs are another example of a vertical hub.
Value Creation
B2B Hubs - Business to Business hubs
What is the purpose and what are the main characteristics of B2B Hubs?
Business-to-business (B2B) hubs, also known as B2B exchanges or marketplaces, are platforms that facilitate commercial transactions and collaborations between businesses. They serve as a centralized digital location where businesses can connect, engage, transact, and share information.
The purpose of B2B hubs is multifold:
The main characteristics of B2B hubs include:
In summary, B2B hubs are digital platforms that enable business transactions and collaborations between companies. They streamline processes, expand market reach, reduce costs, enhance transparency, and foster collaboration. The hubs offer a centralized, secure platform with standardized processes, integration capabilities, and a wide range of services to cater to diverse business needs.
The purpose of B2B hubs is multifold:
- Streamlining Transactions: They provide a structured environment to conduct business, offering standardized processes that simplify transactions, reduce errors, and increase efficiency.
- Increasing Market Reach: By connecting businesses from various regions and industries, these platforms expand market reach and facilitate the discovery of new business opportunities.
- Reducing Costs: B2B hubs often reduce costs related to procurement, sales, and marketing by minimizing manual processes and maximizing economies of scale.
- Improving Market Transparency: B2B hubs offer a more transparent marketplace by providing comprehensive information about products, services, and suppliers.
- Enhancing Collaboration: These platforms also foster better collaboration and communication between businesses, including sharing forecasts, inventory data, and demand information.
The main characteristics of B2B hubs include:
- Centralized Platform: B2B hubs provide a central, online platform for businesses to conduct commercial transactions. They consolidate various business processes into one digital location, improving efficiency and ease of use.
- Multi-Sided Network: B2B hubs connect multiple businesses (buyers, sellers, suppliers, distributors) creating a network effect. As more businesses join the hub, the value of the platform increases for all participants.
- Standardized Processes: These hubs offer standardized methods for conducting business transactions, facilitating interoperability, and improving efficiency.
- Security and Compliance: B2B hubs typically offer robust security features and adhere to compliance regulations to protect the integrity and confidentiality of business transactions.
- Integration Capabilities: B2B hubs can often be integrated with other business systems such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) or Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software, facilitating seamless data exchange.
- Range of Services: Depending on their specific focus, B2B hubs may offer a wide range of services, including product listing, order management, supply chain management, electronic invoicing, payment services, and analytics.
In summary, B2B hubs are digital platforms that enable business transactions and collaborations between companies. They streamline processes, expand market reach, reduce costs, enhance transparency, and foster collaboration. The hubs offer a centralized, secure platform with standardized processes, integration capabilities, and a wide range of services to cater to diverse business needs.
A B2B Hub is an online market place where
- suppliers,
- Vendors and
- clients
Examples of Vertical and Horizontal Hubs
Click on the links below to see examples of vertical and horizontal hubs:
Site Enhancements
Many sites make enhancements on an ongoing basis that reclassify their e-business model.
Find out what a site and company is about by visiting the site's "About Us" pages where available.
Find out what a site and company is about by visiting the site's "About Us" pages where available.
Question: How might one classify a website that operates across industry verticals to:
- Provide information, analysis, resources and connections to the people who build and grow net markets, as well as to the broader community of investors, technology providers and others who facilitate this growth
- Bring together market makers, software vendors, analyst or investor, Net Market Makers
Answer: The website may be termed a "Hub of Hubs"
Another commonly used e-business primary model is B2C. The next lesson discusses the variations on this primary model.
Selecting e-business Model - Exercise
Click the Exercise link below to apply what you have learned about B2B models and commerce.
Selecting Ebusiness Model - Exercise
Selecting Ebusiness Model - Exercise
[1]Hub: A business that connects multiple buyers and sellers together electronically