| Lesson 2 | Purposes of security |
| Objective | Identify the need for secure electronic transactions. |
Purposes of Security in ecommerce
When you visit a well-designed e-commerce site you can peruse the available goods and services, review pricing and delivery terms, add items to a shopping cart (or some equivalent to a shopping cart), make payments, and track delivery. The entire system that delivers the e-commerce site and all its functions probably use several different security techniques, though it may be transparent to the customer.
- Essential Purposes of Security
In e-commerce, security usually involves five essential purposes, including- data confidentiality,
- authentication and certification,
- access control[1],
- data integrity, and
- non-repudiation.
These are described in the table below.
Secure Electronic Transactions are vital to protect Sensitive Data
In eCommerce, secure electronic transactions are vital to protect sensitive data and maintain the trust of users. The three essential components—Data Confidentiality, Identification (Authentication and Certification), and Data Integrity—ensure the security of these transactions. Here's how each of these components contributes to the overall security:
Summary of Their Importance in eCommerce:
Together, these components form the backbone of secure electronic transactions in eCommerce, ensuring a safe and trusted environment for online shopping and payments.
- Data Confidentiality
- Purpose: Protects sensitive information from unauthorized access during the transaction process.
- How It Works: Data confidentiality ensures that sensitive information, such as credit card numbers, personal details, and payment data, is encrypted during transmission and storage. Only the intended recipient, typically the merchant or payment processor, can access the information.
- Importance in eCommerce: Customers are required to share private information such as addresses, payment details, and passwords. By ensuring confidentiality through encryption technologies like SSL/TLS, eCommerce platforms can protect customers from data breaches, ensuring privacy and compliance with regulations (e.g., GDPR, PCI-DSS).
- Identification (Authentication and Certification)
- Purpose: Verifies the identities of both parties involved in the transaction (customer and merchant) to prevent fraud.
- How It Works: Authentication ensures that the entities participating in the transaction are who they claim to be. Certification Authorities (CAs) issue digital certificates to validate the identity of websites and parties involved in the transaction. For example, SSL certificates confirm the authenticity of an eCommerce website, ensuring customers are interacting with a legitimate entity.
- Importance in eCommerce: Authentication prevents fraud and phishing attacks by ensuring that both customers and merchants can trust each other's identities. Multi-factor authentication (MFA), digital signatures, and certificates (like SSL certificates) ensure that no unauthorized parties can intervene or impersonate either side of the transaction.
- Data Integrity
- Purpose: Ensures that the data transmitted or received during a transaction is accurate, complete, and has not been altered in transit.
- How It Works: Data integrity is maintained by using hashing algorithms and message digests (e.g., SHA-256), which allow both the sender and receiver to verify that the data has not been tampered with. If even a small change is made to the data, the hash will differ, indicating corruption or manipulation.
- Importance in eCommerce: Integrity guarantees that the transaction data—such as the order details, shipping address, or payment amount—has not been modified by malicious entities during transmission. Without this protection, cybercriminals could alter key transaction details, potentially leading to financial loss or fraud.
Summary of Their Importance in eCommerce:
- Data Confidentiality safeguards private information, preventing data breaches and maintaining customer trust.
- Identification (Authentication and Certification) prevents fraud by ensuring both the customer and the merchant are legitimate participants in the transaction.
- Data Integrity ensures the accuracy and reliability of transaction data, preventing unauthorized alterations that could result in fraud or losses.
Together, these components form the backbone of secure electronic transactions in eCommerce, ensuring a safe and trusted environment for online shopping and payments.
Secure ecommerce Transactions
| Purposes of security | Description |
|---|---|
| Data confidentiality | Much of the data and content you view on an e-commerce site has been secured. The degree of confidentiality of the data and content determines the level of security required. From a business perspective, make sure that sensitive information receives a higher degree of protection. |
| Identification: Authentication and Certification | The Internet is by nature an anonymous medium, and this anonymity affects e-commerce. Identification ensures that someone is who he or she claims to be. This requirement is tantamount when high priced transactions, high volume transactions, or transactions that involve the exchange of sensitive information are involved. Identification techniques include such things as as public-key encryption, certificates, and digital signatures. These are described in detail later in the course. To prevent unauthorized access to or from a private network, firewalls are used. Access to resources behind firewalls typically involves some kind of user access control technique, such as a userid and password; these are often used for data confidentiality also. |
| Data integrity | Data integrity ensures that information has not been modified in transit to the destination. An electronic payment system should ensure data integrity using message digests or hash algorithms. These terms are explained in a later lesson. |
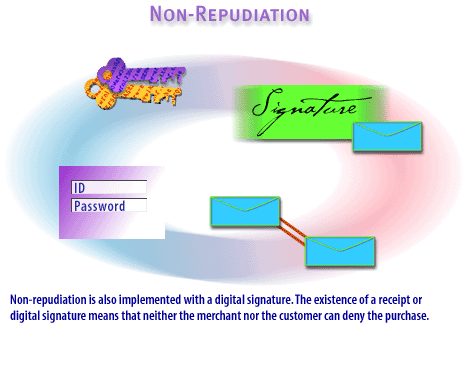
| Non-repudiation | Non-repudiation is the proof that a transaction has been conducted between two specific parties; this is important to prevent merchants or customers from denying a sale or purchase. Non-repudiation may take several forms. A receipt issued to a customer is proof of purchase. Establishing similar forms of non-repudiation is important for e-commerce. |
ecommerce Management
Secure electronic transactions are implemented in various ways, with each of these five purposes in mind. The implementation of security is described in the following series of images.
Data Confidentiality
In the next lesson, you will learn about encryption and decryption.
Security Purpose - Quiz
Click the Quiz link below to test your understanding of the purposes of security.
Security Purpose - Quiz
Security Purpose - Quiz
[1]Access control: Access control governs what resources a user or service may access on the system or network. It protects against the unauthorized use of resources.