Intrinsic operations of SQL Gateways
As an e-business solutions architect, you're sailing through the vast ocean of the digital world. Picture yourself as a master of the vessel, navigating through the waves of data. Your compass? SQL Gateways.Now, imagine SQL Gateways as mystical portals in the world of databases. They serve as bridges, connecting different realms, which in our world, are disparate databases. To operate these gateways, you need a deep understanding of their intrinsic operations - operations that form the heart of these enchanted portals. The first intrinsic operation? Connection. Like an invisible thread that binds our world with the realm beyond the portal, an SQL Gateway establishes a connection with a target database. Whether it's Oracle, MySQL, or SQL Server, it stretches its arms wide open, embracing the data residing in these foreign lands. But it doesn't stop there. Oh no! It ensures these connections are secure, and the passage is safe, with security protocols like SSL encryption and SASL authentication.
Next up, it's the magical process of query translation. Picture a translator in an ancient marketplace, proficient in multiple languages. SQL Gateway is that translator for us, proficient in the languages of different databases. It takes the SQL dialect we speak, and with a wave of its wand, translates it into a dialect that the target database comprehends. This power of translation ensures seamless interaction between databases that otherwise, might stand divided by their SQL dialects.
The third operation is schema mapping. Think of this as a mapmaker, creating detailed maps of uncharted territories. SQL Gateway extracts metadata from the target database and creates a map - a schema that defines the structure of the database. This schema serves as a guide, helping applications navigate through the maze of tables, views, and stored procedures in the database.
Now, on to data transfer, the lifeblood of an SQL Gateway. Like an enchanted river carrying treasures across realms, SQL Gateway transports data between the client application and the target database. It ensures that the flow is not disrupted, handling issues like network failures and inconsistencies in data type with grace and poise. Lastly, an SQL Gateway is also a vigilant guard, maintaining session states for every client. Just as a dutiful guard keeps a record of every visitor entering a kingdom, the gateway tracks active sessions, remembering who is connected and what actions they have performed. This careful record-keeping allows it to handle complex scenarios, like rolling back transactions if necessary.
Intricate, isn't it? But that's the art and science of SQL Gateways. They serve as the grand maestro, orchestrating this symphony of operations to enable seamless data interactions in our digital world. As an e-business solutions architect, your role is to master these operations, unlocking the true potential of SQL Gateways, creating harmony in the cacophony of data, and bringing forth the melody of efficient, reliable, and secure e-business solutions.
Next up, it's the magical process of query translation. Picture a translator in an ancient marketplace, proficient in multiple languages. SQL Gateway is that translator for us, proficient in the languages of different databases. It takes the SQL dialect we speak, and with a wave of its wand, translates it into a dialect that the target database comprehends. This power of translation ensures seamless interaction between databases that otherwise, might stand divided by their SQL dialects.
The third operation is schema mapping. Think of this as a mapmaker, creating detailed maps of uncharted territories. SQL Gateway extracts metadata from the target database and creates a map - a schema that defines the structure of the database. This schema serves as a guide, helping applications navigate through the maze of tables, views, and stored procedures in the database.
Now, on to data transfer, the lifeblood of an SQL Gateway. Like an enchanted river carrying treasures across realms, SQL Gateway transports data between the client application and the target database. It ensures that the flow is not disrupted, handling issues like network failures and inconsistencies in data type with grace and poise. Lastly, an SQL Gateway is also a vigilant guard, maintaining session states for every client. Just as a dutiful guard keeps a record of every visitor entering a kingdom, the gateway tracks active sessions, remembering who is connected and what actions they have performed. This careful record-keeping allows it to handle complex scenarios, like rolling back transactions if necessary.
Intricate, isn't it? But that's the art and science of SQL Gateways. They serve as the grand maestro, orchestrating this symphony of operations to enable seamless data interactions in our digital world. As an e-business solutions architect, your role is to master these operations, unlocking the true potential of SQL Gateways, creating harmony in the cacophony of data, and bringing forth the melody of efficient, reliable, and secure e-business solutions.
How do SQL Gateways work?
How do SQL gateways work? Much like any gateway that is used in networking, a SQL gateway hides the
underlying physical access to data sources from the data requestor and manages database connections. It does this in a few steps:
- Takes an incoming query
- Makes sure the appropriate databases are connected
- Forwards the query, receives query results
- Forwards those to the requestor
Website Layers
As a website becomes more complex, a robust and efficient mechanism for the separation of
- content,
- presentation, and
- logic
Web Application Servers
Web application servers are Web sites that are more interactive, access large amounts
of data, and provide a rich functionality similar to that of desktop applications. Unlike desktop applications, where
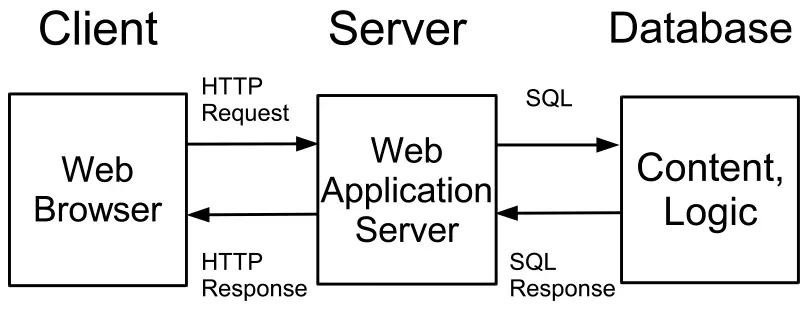
all components are stored and executed on the same computer, Web applications usually follow a three-tier client/-
server architecture (see Figure 5) consisting of the Web browser, the Web server, and a database. All content and
logic are stored in the database and are retrieved and processed as necessary on the Web server. The presentation
information can be embedded with the content or stored as a separate style sheet on the database or the server.
Usually a Web application server interfaces with a relational database, which stores data in rows of tables.
The other major type of database is the object-oriented database, which stores data by encapsulating them into objects. Relational databases are often more efficient and faster than equivalent object-oriented databases and support an almost universal database language, SQL (structured query language). The major disadvantage of developing with Web application servers, besides the inherent complexity, is the necessity of learning a nonstandard or proprietary serverside programming interface or language. There are several majorWeb application servers that support standard programming languages such as Java and C++, but each has
its own application programming interface (API).