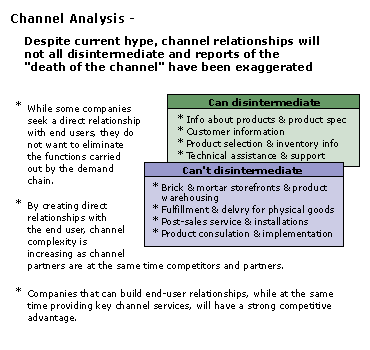
Myth of channel death
Merits of B2B E-commerce
B2B e-commerce in general exposes a selling/buying company to a larger pool of suppliers and corporate buyers.
Transactions over the Internet help overcome the geographical barrier, bringing business partners from all over the world to the e-marketplace.
A company may benefit from transactions with business partners beyond the local market.
The Web-based technology of e-commerce helps minimize the human error found in the paper-based activities and supports timely, if not real-time, communication between and among partners. Different from traditional, costly telecommunications networks, web-based technology makes transactions over the Internet affordable to most businesses involved in the e-marketplace. Also, the existence of many intermediaries also provides interested businesses with low-cost solutions for implementing a B2B e-commerce model.
The Web-based technology of e-commerce helps minimize the human error found in the paper-based activities and supports timely, if not real-time, communication between and among partners. Different from traditional, costly telecommunications networks, web-based technology makes transactions over the Internet affordable to most businesses involved in the e-marketplace. Also, the existence of many intermediaries also provides interested businesses with low-cost solutions for implementing a B2B e-commerce model.
B2B e-commerce models
B2B ecommerce models address the concerns about the effectiveness and efficiency of the supply chain management of business partners and suppliers as well as company buyers. Supply chain management coordinates business activities from order generation, order taking to order distribution of goods/services for individual as well as corporate customers.
Interdependencies in the supply chain create an extended boundary that goes far beyond an individual firm, so that individual firms can no longer maximize their own competitive advantage and therefore profit from cutting costs/prices. Material suppliers and distribution-channel partners, such as wholesalers, distributors, and retailers, all play important roles in supply chain management. B2B ecommerce models address the creation of partnerships with other parties along the supply chain, upstream as well as downstream, to share information of mutual benefit about the need of final customers. The key issue is that all upstream and downstream business activities should be coordinated to meet effectively the demand of final customers. Each partner in the stream should coordinate ts own production/business plans (order fulfillment, procurement, production, and distribution) with those of the other partners so that sufficient streams of goods/services will reach customers in the right place at the right time.
B2B business models also address issues of customer relationship management, the front-end function of a supply chain. An effective business model helps in creating more loyal customers who are not inclined to shop for lower prices but rather who pay for quality and service, in retaining valued customers, and in developing new customers by providing them with new quality products and services. The customer base could be segmented on history of performance in sales/purchases. This information will serve as a basis for promotion and discount, promoting the loyalty of current customers.
Interdependencies in the supply chain create an extended boundary that goes far beyond an individual firm, so that individual firms can no longer maximize their own competitive advantage and therefore profit from cutting costs/prices. Material suppliers and distribution-channel partners, such as wholesalers, distributors, and retailers, all play important roles in supply chain management. B2B ecommerce models address the creation of partnerships with other parties along the supply chain, upstream as well as downstream, to share information of mutual benefit about the need of final customers. The key issue is that all upstream and downstream business activities should be coordinated to meet effectively the demand of final customers. Each partner in the stream should coordinate ts own production/business plans (order fulfillment, procurement, production, and distribution) with those of the other partners so that sufficient streams of goods/services will reach customers in the right place at the right time.
B2B business models also address issues of customer relationship management, the front-end function of a supply chain. An effective business model helps in creating more loyal customers who are not inclined to shop for lower prices but rather who pay for quality and service, in retaining valued customers, and in developing new customers by providing them with new quality products and services. The customer base could be segmented on history of performance in sales/purchases. This information will serve as a basis for promotion and discount, promoting the loyalty of current customers.